Moody’s downgrading India’s sovereign rating has been all over the news. Let’s discuss sovereign credit ratings in detail.
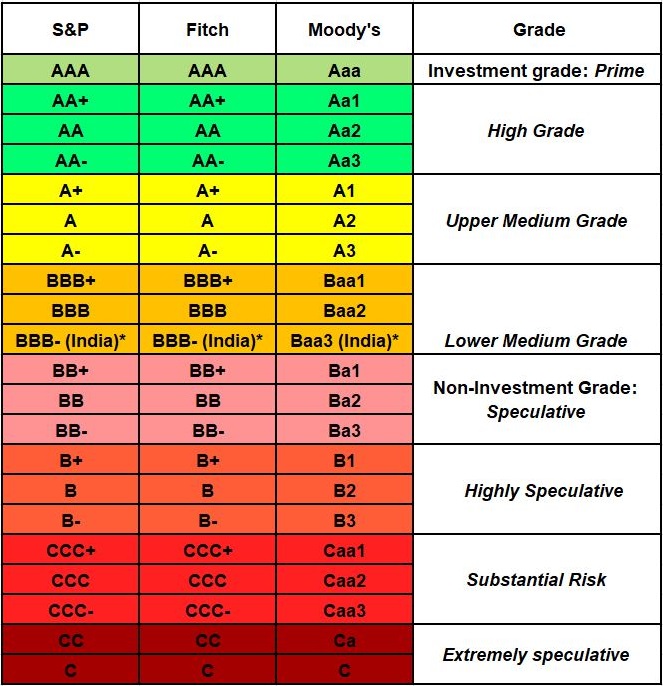
Sovereign credit rating assesses the credit worthiness of a country or a sovereign entity. It helps the investors to assess the risk associated with investing in a particular country. The credit rating agency evaluates country’s economic and political environment to assign a rating. Various indicators will be used to capture the debt characteristics, economic performance, monetary environment, government budget, foreign trade, domestic and external political characteristics to arrive at the rating. The three major credit rating agencies are- Moody’s, Fitch and S&P.
Moody’s, Fitch and S&P Long Term Rating Scale
The rating scale is divided into ‘Investment grade’ and ‘Non-investment grade’, where the former signifies relatively low risk of default and latter signifies high risk. Both categories are again divided into four sub-levels.
In addition to rating decisions, credit rating agencies also provide credit outlook. It predicts the future trend in credit rating and is divided into three types: negative, stable, and positive.
Credit History of India:
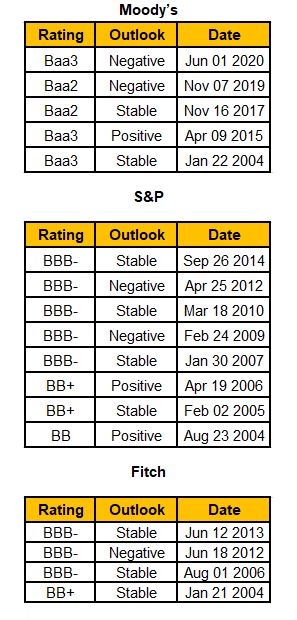
Latest Developments:
- Moody’s has downgraded India’s sovereign rating to ‘Baa3’ with a negative outlook
- Moody’s rating for India is now in line with Fitch’s and S&P’s rating at ‘BBB- ‘
- In December 2019, Fitch has reaffirmed India’s ‘BBB- ‘rating with a stable outlook
- In February 2020, S&P has reaffirmed India’s ‘BBB- ‘rating with a stable outlook









